
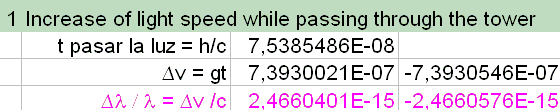

A gravitational uphill for light coming from distant galaxies causes a redshift far more dominant than the cosmological redshift. As a feature of the model the gravitational constant G is inversely proportional to the scale factor a. It is assumed that expansion is caused by the continuous addition of matter, due to, say, electron-positron fluctuations. The model offers a tool to investigate the present state of the universe. The set of equations is called the CBU model (Continuously Breeding Universe). Further, a theory which replaces the cosmological constant with the momentum pressure of emerging matter has been developed. Geodetic Survey of NIST and JILA Clock Laboratories, Boulder, Colorado (NOAA, 2019).A study based on a new formulation of the Friedmann-Lemaître-Robertson-Walker equation has led to an alternative scenario for the evolving universe. Operational magic intensity for Sr optical lattice clocks. A quantum many-body spin system in an optical lattice clock. Nuclear spin effects in optical lattice clocks. Observation and cancellation of a perturbing dc Stark shift in strontium optical lattice clocks. Lodewyck, J., Zawada, M., Lorini, L., Gurov, M. Hyperpolarizability effects in a Sr optical lattice clock. Differential clock comparisons with a multiplexed optical lattice clock. Cavity-QED measurements of the 87Sr millihertz optical clock transition and determination of its natural linewidth. Hamiltonian engineering of spin-orbit coupled fermions in a Wannier-Stark optical lattice clock. Optical lattice clock with atoms confined in a shallow trap. Observation of atomic Wannier–Stark ladders in an accelerating optical potential. Dynamics of interacting fermions under spin–orbit coupling in an optical lattice clock. Spin–orbit-coupled fermions in an optical lattice clock. (eds) Observation of the System Earth from Space: CHAMP, GRACE, GOCE and Future Missions (Springer, 2014). Geodesy and metrology with a transportable optical clock. SAGE: a proposal for a space atomic gravity explorer. Laurent, P., Massonnet, D., Cacciapuoti, L. Test of general relativity by a pair of transportable optical lattice clocks. Gravitational wave detection with optical lattice atomic clocks.

Frequency ratio measurements at 18-digit accuracy using an optical clock network. Precision metrology meets cosmology: improved constraints on ultralight dark matter from atom-cavity frequency comparisons. Optical clock comparison for Lorentz symmetry testing. Search for new physics with atoms and molecules. Half-minute-scale atomic coherence and high relative stability in a tweezer clock. Quantum network of atom clocks: a possible implementation with neutral atoms. Variational spin-squeezing algorithms on programmable quantum sensors. Entanglement on an optical atomic-clock transition. Imaging optical frequencies with 100 μHz precision and 1.1 μm resolution. JILA SrI optical lattice clock with uncertainty of 2.0 × 10 −18. 27Al + quantum-logic clock with a systematic uncertainty below 10 −18. Atomic clock performance enabling geodesy below the centimetre level. Systematic evaluation of an atomic clock at 2 × 10 −18 total uncertainty. Demonstration of 4.8 × 10 −17 stability at 1 s for two independent optical clocks. A Fermi-degenerate three-dimensional optical lattice clock. Gravitational redshift test using eccentric Galileo satellites. Test of the gravitational redshift with Galileo satellites in an eccentric orbit. Grundgedanken der allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie und Anwendung dieser Theorie in der Astronomie.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
